
Red coloration around the stone (Cs) is a unique phenomenon in peach. It happens due to the accumulation of anthocyanin and is associated with fruit ripening. However, it is not clear how the anthocyanin accumulates surrounding the stone.
Now, researchers led by Prof. HAN Yuepeng and research assistant ZHAO Lei from the Wuhan Botanical Garden of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have revealed that the PpHY5 gene participates in the regulation of the Cs trait, and its expression was consistent with anthocyanin accumulation surrounding the stone.
The study was published in The Plant Journal on March 15.
The researchers found that PpHY5 promoted the activation of anthocyanin regulator gene PpMYB10.1 in the presence of a cofactor PpBBX10. However, an E3 ubiquitin ligase gene PpCOP1 was moderately expressed in the flesh around the stone at the later stages of fruit development and could interact with PpHY5 to repress its activation for PpMYB10.1 gene.
This study firstly reveals the PpHY5 gene is involved in the anthocyanin accumulation surrounding the stone, which is helpful for comprehensive understanding of the complex mechanisms underlying anthocyanin accumulation in peach fruit.
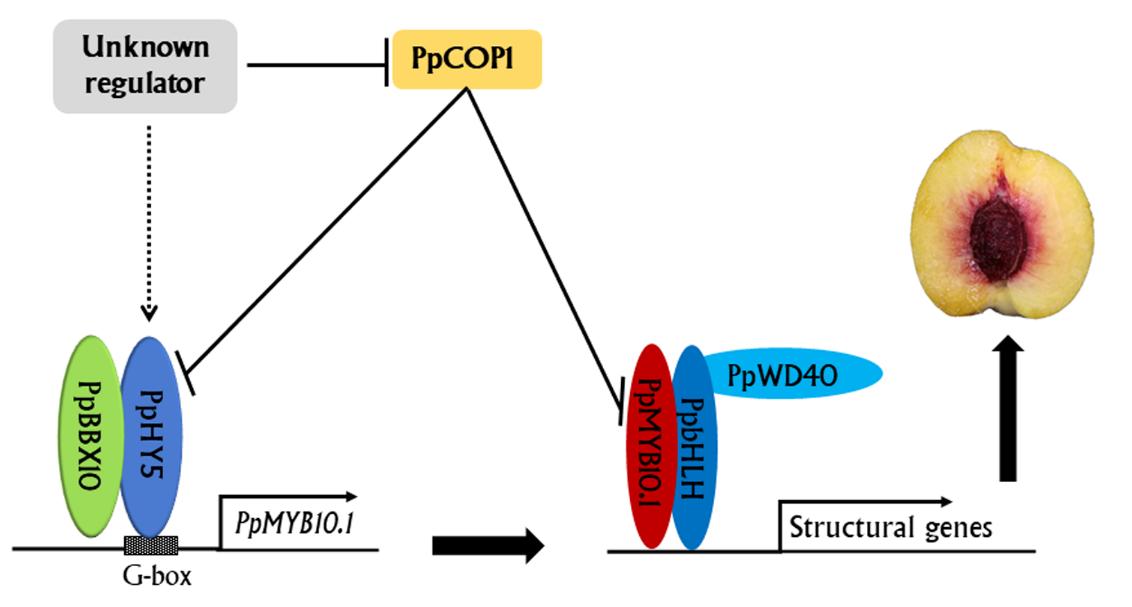
The regulatory network model for PpHY5 involved in anthocyanin coloration in the peach flesh surrounding the stone (Image by ZHAO Lei)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

